Large language models (LLMs), including GPT-3, PaLM, OPT, BLOOM, and GLM-130B, have greatly pushed the limits of what is possible for computers to comprehend and produce in terms of language. One of the most fundamental language applications, question answering, has been significantly improved due to recent LLM breakthroughs. According to existing studies, the performance of LLMs’ closed-book QA and in-context learning QA is on par with that of supervised models, which contributes to our understanding of LLMs’ capacity for memorization. But even LLMs have a finite capacity, and they fall short of human expectations when faced with problems that need considerable exceptional knowledge. Therefore, recent attempts have concentrated on building LLMs enhanced with external knowledge, including retrieval and online search.
For instance, WebGPT is capable of online browsing, lengthy answers to complicated inquiries, and equally helpful references. Despite its popularity, the original WebGPT approach has yet to be widely adopted. First, it relies on many expert-level annotations of browsing trajectories, well-written responses, and answer preference labeling, all of which require expensive resources, a lot of time, and extensive training. Second, by telling the system to interact with a web browser, give operation instructions (such as “Search,” “Read,” and “Quote”), and then gather pertinent material from online sources, the behavior cloning approach (i.e., imitation learning) necessitates that its basic model, GPT-3, resemble human experts.
Finally, the multi-turn structure of web surfing necessitates extensive computational resources and can be excessively sluggish for user experience for example, it takes WebGPT-13B around 31 seconds to respond to a 500-token query. Researchers from Tsinghua University, Beihang University and Zhipu.AI introduce WebGLM in this study, a sound web-enhanced quality assurance system built on the 10-billion-parameter General Language Model (GLM-10B). Figure 1 shows an illustration of one. It is effective, affordable, sensitive to human preferences, and most significantly, it is of a caliber that is on par with WebGPT. To attain good performance, the system uses several novel approaches and designs, including An LLM-augmented Retriever, a two-staged retriever that combines fine-grained LLM-distilled retrieval with a coarse-grained web search.
The capacity of LLMs like GPT-3 to spontaneously accept the right references is the source of inspiration for this technique, which might be refined to enhance smaller dense retrievers. A GLM-10B-based response generator bootstrapped via LLM in-context learning and trained on quoted long-formed QA samples is known as a bootstrapped generator. LLMs may be prepared to provide high-quality data using adequate citation-based filtering instead of relying on expensive human experts to write in WebGPT. A scorer that is taught using user thumbs-up signals from online QA forums can understand the preferences of the human majority when it comes to various replies.
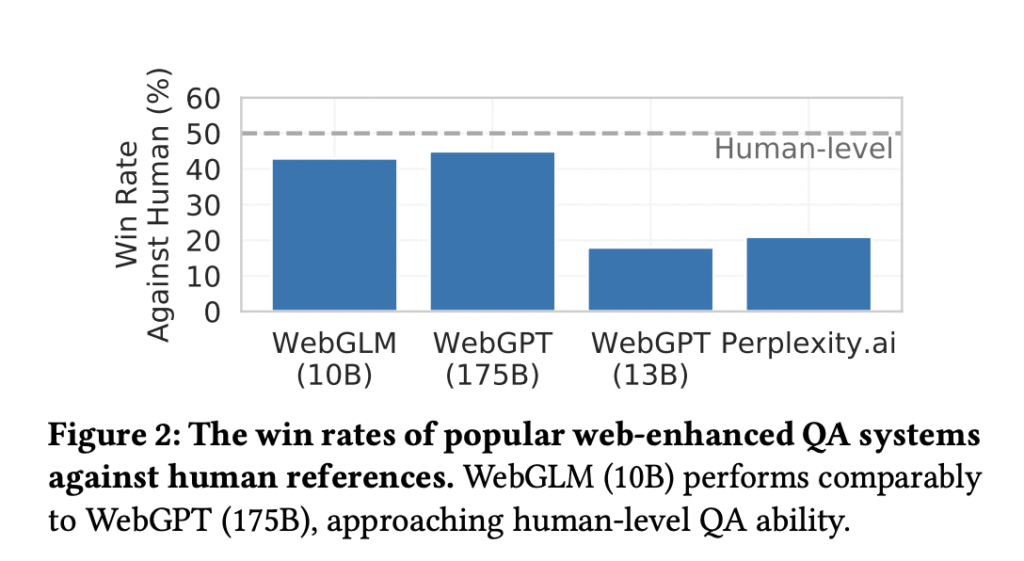
They demonstrate that a suitable dataset architecture might produce a high-quality scorer compared to WebGPT’s expert labeling. The results of their quantitative ablation tests and in-depth human evaluation show how efficient and effective the WebGLM system is. In particular, WebGLM (10B) outperforms WebGPT (175B) on their Turing test and outperforms the similarly sized WebGPT (13B). WebGLM is one of the greatest publicly available web-enhanced QA systems as of this submission, thanks to its enhancement over the only publicly accessible system, Perplexity.ai. In conclusion, they provide the following in this paper: • They build WebGLM, an effective web-enhanced quality assurance system with human preferences. It performs similarly to WebGPT (175B) and substantially better than WebGPT (13B), a similar size.
It also surpasses Perplexity.ai, a popular system powered by LLMs and search engines. • They identify WebGPT’s limitations on real-world deployments. They propose a set of new designs and strategies to allow WebGLM’s high accuracy while achieving efficient and cost-effective advantages over baseline systems. • They formulate the human evaluation metrics for evaluating web-enhanced QA systems. Extensive human evaluation and experiments demonstrate WebGLM’s strong capability and generate insights into the system’s future developments. The code implementation is available on GitHub.
Check Out The Paper and Github. Don’t forget to join our 24k+ ML SubReddit, Discord Channel, and Email Newsletter, where we share the latest AI research news, cool AI projects, and more. If you have any questions regarding the above article or if we missed anything, feel free to email us at Asif@marktechpost.com
Featured Tools From AI Tools Club
🚀 Check Out 100’s AI Tools in AI Tools Club
Aneesh Tickoo is a consulting intern at MarktechPost. He is currently pursuing his undergraduate degree in Data Science and Artificial Intelligence from the Indian Institute of Technology(IIT), Bhilai. He spends most of his time working on projects aimed at harnessing the power of machine learning. His research interest is image processing and is passionate about building solutions around it. He loves to connect with people and collaborate on interesting projects.